A) $500.
B) $400.
C) $350.
D) $300.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the same for monopoly and competition under the same cost and demand conditions?
A) The amount of output that is produced.
B) Economic profits.
C) The goal of maximizing profits.
D) Efficiency of production at the profit-maximizing output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Table 24.1 Monopoly Costs and Revenue In Table 24.1,the maximum profit that can be achieved is
A) -$200.
B) $100.
C) $250.
D) $500.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a barrier to entry into a monopoly market?
A) Economic profits for the monopolist.
B) Economies of scale.
C) A large number of firms in the industry.
D) Production of a homogeneous product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is likely to be a monopolist?
A) A drug firm that has a patent granting it the exclusive right to produce a drug.
B) A large firm like GM,which has a substantial portion of the car market.
C) The Boeing Company,which is one of the largest producers of airplanes.
D) An Indonesian restaurant in a large city.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following prohibits exclusive dealing?
A) The Sherman Act.
B) The Clayton Act.
C) The Federal Trade Commission Act.
D) Case decisions,such as those for AT&T and IBM.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is true about the output level where marginal revenue equals marginal cost?
A) Economic profits are equal to zero.
B) The firm should increase its output.
C) The firm is maximizing profit.
D) The firm should reduce its output.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopoly
A) Maximizes profits at the output level where P = MC.
B) Is one of many sellers in a given market.
C) Charges higher prices than competitive firms,ceteris paribus.
D) Maximizes profits at the output level where P = MR.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a company is the sole U.S.producer of good X,the market may still be contestable because of all but which one of the following?
A) Foreign producers can provide good X to the U.S.market.
B) Many domestic firms can potentially begin production of good X.
C) New technology may threaten to make good X obsolete.
D) The presence of a government franchise.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
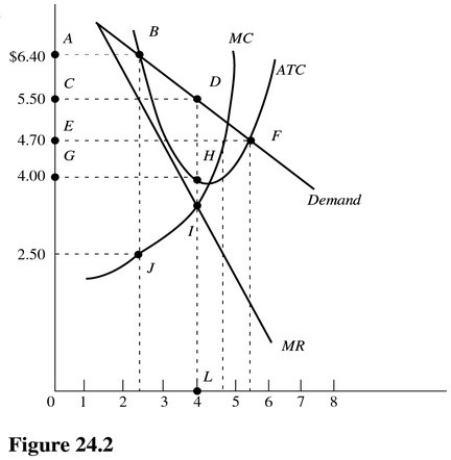 In Figure 24.2,total profit at the profit-maximizing rate of output is
In Figure 24.2,total profit at the profit-maximizing rate of output is
A) $16.00.
B) $5.50.
C) $6.00.
D) $22.00.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The World View article titled "Russia's Sable Monopoly Persists" provides evidence that Russia experienced
A) Barriers to entry.
B) Economies of scale.
C) Negative economic profit.
D) Price discrimination.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A barrier to entry is
A) A law established by the government to protect new industries.
B) A commitment on the part of big business to allow smaller companies to compete.
C) An obstacle that prevents additional workers from entering an industry,such as a union.
D) An obstacle that makes it difficult for new firms to enter a market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a firm can change market prices by altering its output,then it
A) Has market power.
B) Faces a flat demand curve.
C) Is a price taker.
D) Engages in marginal cost pricing.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price discrimination does not allow a producer to
A) Obtain greater total revenue.
B) Charge both higher and lower prices.
C) Obtain higher profits.
D) Designate a point above the market demand curve as the new equilibrium.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a contestable market,
A) An imperfectly competitive industry does not face any potential competition when profits increase.
B) There are economies of scale that heighten competition.
C) Barriers to entry and long-run economic profits are low.
D) Many firms compete in producing a standardized product.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Price-discriminating firms that sell in two markets will charge higher prices in the market,ceteris paribus,
A) With a higher positive cross-price elasticity of demand with respect to substitutes.
B) With the more price-inelastic demand.
C) With the more income-elastic demand.
D) With lower incomes.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
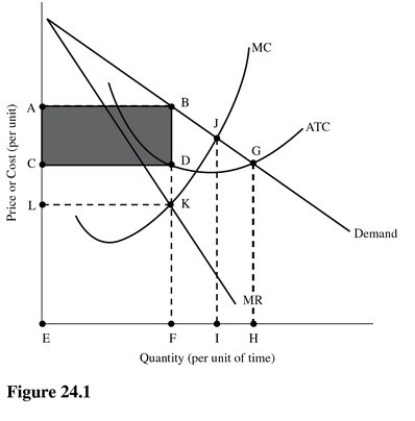 In Figure 24.1,total revenue is represented by the area
In Figure 24.1,total revenue is represented by the area
A) ABFE.
B) CDFE.
C) ABGHE.
D) ABDC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are limitations on the market power of a monopoly except
A) The elasticity of demand.
B) The inability of a firm to control demand.
C) The ability of a company to control the quantity supplied.
D) The demand curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is possible for a monopolist to earn an economic loss.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume a monopoly confronts the same costs and demand as a competitive industry.In this case,the monopolist produces
A) The same output and charges the same price as the competitive industry.
B) More output and charges a higher price than the competitive industry.
C) Less output and charges a lower price than the competitive industry.
D) Less output and charges a higher price than the competitive industry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 121 - 140 of 147
Related Exams