A) shaping intangible preferences; predatory pricing
B) the minds of buyers; past habits and advertising
C) imperfect competition; the concept of differentiated products
D) imperfect competition; advertising and consumer habits
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A _______ refers to a group of firms colluding with one another to produce at the monopoly output and sell at the monopoly price.
A) prisoner's dilemma
B) cartel
C) game theory
D) duopoly
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When P > MC in a monopolistically competitive market, that industry will most likely produce _______ than would be found in a perfectly competitive industry. Benefits to society of providing additional quantity as measured by the price that people are willing to pay exceeds the marginal costs to society of producing those units.
A) a higher quantity of a good and charge a lower price
B) the price that people are willing to pay is lower
C) a lower quantity of a good and charge a higher price
D) the price people are willing to pay is not more
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The long-term result of entry and exit in a perfectly competitive market is that all firms end up selling at the price level determined by the lowest point on the
A) total cost curve.
B) average variable cost curve.
C) total marginal cost curve
D) average cost curve.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the framework of monopolistic competition, the way advertising works can be perceived as
A) causing a firm's perceived demand curve to become more elastic.
B) causing a firm's perceived demand curve to become more inelastic.
C) causing demand for the firm's product to increase.
D) causing both b and c to occur.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a perfectly competitive market involves many firms selling identical products, then, in the face of such competition,
A) each of these firms must act as a price-maker.
B) each of these firms must act as a price-taker.
C) collusion amongst them will most often result.
D) demand curves can become kinked in appearance.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a monopoly or a monopolistic competitor raises their prices, then
A) decline in quantity demanded will be larger for the monopoly.
B) decline in quantity demanded will be larger for the monopolistic competitor.
C) the quantity demanded for the monopoly product falls to zero.
D) the quantity demanded for the monopolistic competitor will fall to zero.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the firm is producing at a quantity of output where marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost, then,
A) the firm's perceived demand will shift to the left.
B) the firm should keep expanding production.
C) each marginal unit adds profit by bringing in less revenue than its cost.
D) the firm is now earning zero for profit.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolistic competitor has the following information about cost and demand.
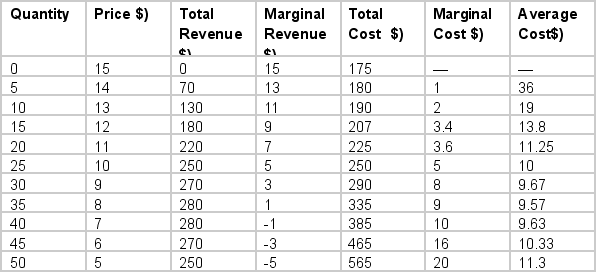 If this industry was perfectly competitive, what price would the good sell for?
If this industry was perfectly competitive, what price would the good sell for?
A) $8
B) $9
C) $10
D) $11
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The desire of businesses to _______, so that they can raise the prices that they charge and earn higher profits, has been well-understood by economists for a long time.
A) compete with each other
B) engage in free market activities
C) maximize profits for social benefit
D) avoid competing with each other
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The perceived demand curve for a group of competing oligopoly firms will appear kinked as a result of their commitment to
A) match price increases, but not price cuts.
B) stand at opposite ends of the competition spectrum.
C) match price cuts, but not price increases.
D) stand at the high point of the competition spectrum.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The shape of the perceived demand curve for a perfectly competitive firm reflects that firm's ability to
A) sell any quantity it wishes at the prevailing market price.
B) raise its price without losing all of its customers.
C) choose any combination of price and quantity.
D) lose fewer customers than a monopoly that raised its prices.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The branch of mathematics that analyzes situations in which players must make decisions and then receive payoffs most often used by economists is
A) oligopoly collusion.
B) prisoner's dilemma.
C) game theory.
D) collusion theory
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolistically competitive industry does not display _______ in either the short-run, when firms are making _______, nor in the long-run, when firms are earning _______.
A) allocative efficiency; profits and losses; negative profits
B) productive efficiency; profits and losses; zero profits
C) productive and allocative efficiency; profits and losses; zero profits
D) productive and allocative efficiency; profits and losses; negative profits
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a perfectly competitive firm raises its price, the quantity demanded of its product _______.
A) diminishes temporarily in the short run
B) falls to zero
C) stays the same
D) falls below marginal cost
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Monopolistic competitors in the food industry will often include a recyclable symbol on packaging used for their product as a means to
A) be socially responsible.
B) be environmentally responsible.
C) differentiate their product.
D) be perceived more favorably.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Would raising the price for a product create a larger decline in quantity demanded for a monopolistic competitor's than it would for a monopoly?
A) no; a monopolistic competitor perceives demand as a price maker
B) no; conditions of imperfect competition means demand is constant
C) yes; but temporarily because price increases only create a short-run decline
D) yes; consumers will buy from competitors offering lower priced substitutes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Perfect competition and monopoly stand at _______ of the spectrum of competition.
A) opposite ends
B) the high end
C) the low end
D) the mid-way point
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopolistic competitor has the following information about cost and demand.

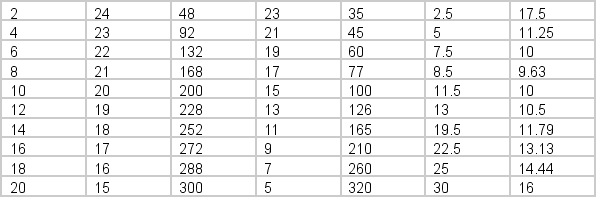 What will the firm's profits equal in the short run?
What will the firm's profits equal in the short run?
A) 0
B) $91
C) $102
D) $228
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Why are the underlying economic meanings of the perceived demand curves for a monopolist and monopolistic competitor different?
A) a monopolist faces the market demand curve and a monopolist competitor does not
B) a monopolist competitor faces the market demand curve and a monopolist does not
C) because the demand curve for a monopolistic competitor is upward sloping
D) because the demand curve perceived by the monopolist is flatter than that of a monopolist competitor
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 79
Related Exams