A) 150 N
B) 15 N
C) 30 N
D) 300 N
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A hoop with a mass of 2.75 kg is rolling without slipping along a horizontal surface with a speed of 4.5 m/s when it starts down a ramp that makes an angle of 2 below the horizontal. What is the Forward speed of the hoop after it has rolled 3.0 m down as measured along the surface of the Ramp?
A) 5.7 m/s
B) 6.3 m/s
C) 4.9 m/s
D) 8.0 m/s
E) 5.2 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
A 350-g air track cart on a horizontal air track is attached to a string that goes over a frictionless pulley with a moment of inertia of and a radius of 1.35 cm. If the string is pulled vertically downward by a force of 2.50 N, (a) what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the cart, and (b) what is the tension in the horizontal string between the pulley and the cart?
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solid uniform cylinder is rolling without slipping. What fraction of its kinetic energy is rotational?
A) 2/3
B) 1/2
C) 1/3
D) 3/4
E) 1/4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The rotating systems shown in the figure differ only in that the two identical movable masses are positioned a distance r from the axis of rotation (left) , or a distance from the axis of rotation (right) . If you release the hanging blocks simultaneously from rest, and call the time taken by the block on the left and the time taken by the block on the right to reach the bottom, respectively, then

A)
B)
C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As you are leaving a building, the door opens outward. If the hinges on the door are on your right, what is the direction of the angular velocity of the door as you open it?
A) down
B) forwards
C) to your right
D) up
E) to your left
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A ballet dancer is spinning in the middle of a horizontal frictionless stage. Which of the following things could he change by moving parts of his body or his whole body? (There could be more than one correct choice.)
A) the horizontal component of his linear momentum
B) his translational kinetic energy
C) his angular momentum
D) his moment of inertia
E) his rotational kinetic energy
F) the location of his center of mass (or center of gravity)
G) his total kinetic energy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
As shown in the figure, a given force is applied to a rod in several different ways. In which case is the torque about the pivot P due to this force the greatest?
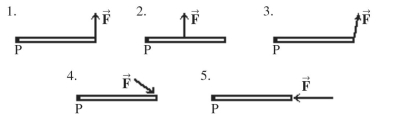
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An ice skater has a moment of inertia of when her arms are outstretched, and at this time she is spinning at 3.0 rev/s. If she pulls in her arms and decreases her moment of inertia to 2.0 how fast will she be spinning?
A) 7.5 rev/s
B) 3.3 rev/s
C) 10 rev/s
D) 2.0 rev/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A mechanic is examining the wheel of a bicycle to adjust the brake. With the bicycle off the ground, he manually rotates the wheel until it reaches an angular speed of 12.0 rad/s and then allows it to coast to a stop. If the wheel has a moment of inertia of and the wheel slows uniformly to a stop in 160 s, what is the magnitude of the retarding torque?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A solid uniform ball with a mass of 125 g is rolling without slipping along the horizontal surface of a table with a speed of 4.5 m/s when it rolls off the edge and falls towards the floor, 1.1 m below. What is the rotational kinetic energy of the ball just before it hits the floor?
A) 1.1 J
B) 0.73 J
C) 2.6 J
D) 0.51 J
E) This question cannot be answered without knowing the radius of the ball.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider a uniform hoop of radius R and mass M rolling without slipping. Which is larger, its translational kinetic energy or its rotational kinetic energy?
A) Translational kinetic energy is larger.
B) Both are equal.
C) Rotational kinetic energy is larger.
D) You need to know the speed of the hoop to tell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To drive a typical car at 40 mph on a level road for one hour requires about of energy. Suppose we tried to store this much energy in a spinning, solid, uniform, cylindrical flywheel. A large flywheel cannot be spun too fast or it will fracture. If we used a flywheel of diameter 1.2 m and mass 400 kg, what angular speed would be required to store
A) 940 rad/s
B) 3600 rad/s
C) 5500 rad/s
D) 530 rad/s
E) 1800 rad/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The drum shown in the figure has a radius of 0.40 m and a moment of inertia of about an axis perpendicular to it through its center. The frictional torque at the drum axle is 14-m length of rope is wound around the rim. The drum is initially at rest. A constant force is applied to the free end of the rope until the rope is completely unwound and slips off. At that instant, the angular speed of the drum is 23 rad/s. The drum then slows down at a constant rate and comes to a halt. In this situation, what was the magnitude of the constant force applied to the rope?
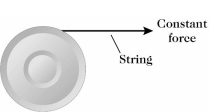
A) 51 N
B) 40 N
C) 18 N
D) 29 N
E) 7.5 N
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A particular motor can provide a maximum torque of 110 N · m. Assuming that all of this torque is used to accelerate a solid, uniform, cylindrical flywheel of mass 10.0 kg and radius 3.00 m, how Long will it take for the flywheel to accelerate from rest to 8.13 rad/s?
A) 4.36 s
B) 4.03 s
C) 2.83 s
D) 3.33 s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A uniform rod is 2.0 m long. It is hinged to a wall at its left end, and held in a horizontal position at its right end by a vertical very light string, as shown in the figure. What is the angular acceleration of the rod at the moment after the string is released if there is no friction in the hinge?
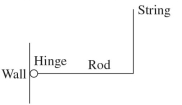
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) It cannot be calculated without knowing the mass of the rod.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a certain cyclotron, a proton of mass moves in a circle of diameter 1.6 m with an angular speed of what is the angular momentum of the proton?
A)
B)
C)
D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At a certain instant, a compact disc is rotating at 210 rpm. What is its angular speed in rad/s?
A) 660 rad/s
B) 22 rad/s
C) 69 rad/s
D) 45 rad/s
E) 11 rad/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A scooter has wheels with a diameter of 120 mm. What is the angular speed of the wheels when the scooter is moving forward at 6.00 m/s?
A) 100 rpm
B) 955 rpm
C) 50.0 rpm
D) 47.7 rpm
E) 72.0 rpm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A man in a gym is holding an 8.0-kg weight at arm's length, a distance of 0.55 m from his shoulder joint. What is the torque about his shoulder joint due to the weight if his arm is horizontal?
A) 43 N · m
B) 0.24 N · m
C) 4.4 N · m
D) 15 N · m
E) 0 N · m
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 61 - 80 of 148
Related Exams