A) DNA is duplicated during the G 1 and G 2 phases
B) DNA replicates during cytokinesis
C) the M phase is usually the longest phase of the cell cycle
D) interphase consists of G 1, S, and G 2
E) the cell enters a non-dividing state in the G 2 phase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When during the cell cycle are chromosomes visible under a microscope?
A) only during interphase
B) only when they are being copied
C) during mitosis
D) only during the G 1 phase
E) chromosomes are always visible
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows a cell in the mitotic stage of 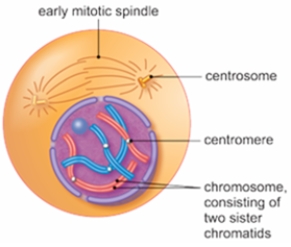
A) anaphase.
B) interphase.
C) metaphase.
D) prophase.
E) telophase.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The term metastasis refers to the fact that cancer cells tend to
A) destroy.
B) divide.
C) decline.
D) shrink.
E) spread.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What structure is formed by two sister chromatids being held together by a centromere?
A) duplicated chromosome
B) chromatin
C) histones
D) nucleosome
E) DNA
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cytokinesis in plants occurs as ________ and in animals as ________.
A) actin fibers pull the membrane inward until the two sides touch; the Golgi apparatus produces membrane-bound vesicles filled with materials to make the cell wall
B) the Golgi apparatus produces membrane-bound vesicles filled with materials to make the cell wall; actin fibers pull the membrane inward until the two sides touch
C) the centrosome produces membrane-bound vesicles filled with materials to make the cell wall; the Golgi apparatus produces actin fibers to pull the membrane inward until the two sides touch
D) actin fibers interact to make the cell wall; the cleavage furrow pulls the membrane inward until the two sides touch
E) the Golgi apparatus produces a cleavage furrow; actin fibers pull the membrane inward until the two sides touch
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an inaccurate statement about mitosis?
A) the cells arising from mitosis are genetically alike
B) the process of nuclear division is followed by cytokinesis
C) spindle fibers are involved in the movement of chromosomes during mitosis
D) both sexually and asexually reproducing organisms utilize the process of mitosis
E) the cells arising from mitosis contain only half of the necessary genetic material
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Proteins that are involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, and that show fluctuation in concentration during the cell cycle, are called
A) centromeres.
B) kinetochores.
C) centrioles.
D) proton pumps.
E) cyclins.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cytokinesis usually, but not always, follows mitosis. If a cell undergoes mitosis and not cytokinesis, this would result in
A) a cell with a single large nucleus.
B) a cell with two nuclei.
C) cells with abnormally small nuclei.
D) feedback responses that prevent mitosis.
E) death of the cell line.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Differentiated cells, such as nerve cells, would be in which of the following stages of the cell cycle?
A) G 1
B) G 0
C) G 2
D) M
E) R
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cells grown in a petri dish tend to divide until they form a thin layer covering the bottom of the dish. Which of the following statements explains why this occurs?
A) The cells become deficient in cyclin.
B) The petri dish inhibits the cells' growth.
C) Cell division can be inhibited by the proximity of other cells of the same type, a process called contact inhibition.
D) Most cells grown in petri dishes have gone through apoptosis.
E) The cells have differentiated into more specialized cells.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the structure that holds together the two sister chromatids that form a chromosome?
A) centromere
B) nucleosome
C) histone
D) nucleus
E) chromatin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What structure holds two sister chromatids together?
A) centromere
B) centriole
C) chromatin
D) spindle
E) centrosome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Cancer is a disorder in which some cells have lost the ability to control their
A) size.
B) spindle fibers.
C) rate of cell division.
D) surface area.
E) volume.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The G 2 checkpoint prevents the cell cycle from continuing until
A) it is known for sure if the cell will divide.
B) the DNA has finished replicating.
C) the chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle fibers.
D) all the organelles have been duplicated.
E) the centrosomes have duplicated.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Embryonic cells and cancer cells are similar because
A) DNA polymerase is inactive.
B) telomerase is active.
C) telomerase is inactive.
D) RNA polymerase is inactive.
E) proto-oncogenes are inactive.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The presence of which protein is required in order for chromatin to compact correctly within the nucleus?
A) histone
B) nucleosome
C) actin
D) chromatid
E) myosin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The figure below shows a cell in which stage of the cell cycle? 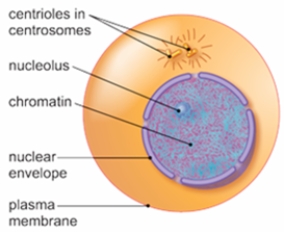
A) anaphase
B) interphase
C) metaphase
D) prophase
E) telophase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During which stage of the cell cycle do the chromosomes duplicate?
A) interphase: S
B) interphase: G 1
C) interphase: G 2
D) prophase
E) telophase
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Cancer cells have abnormal chromosomes because they express telomerase when they should not.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 75
Related Exams