A) a compound.
B) an isotope.
C) an element.
D) a molecule.
E) both an element and a molecule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unstable isotopes can be useful
A) catalysts.
B) in medical diagnosis.
C) in vitamins.
D) in the formation of hydrogen bonds.
E) as buffers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would NOT normally be found as a component of a cell's nucleic acids?
A) adenine deoxyribonucleotides
B) thymine deoxyribonucleotides
C) uracil deoxyribonucleotides
D) cytosine ribonucleotides
E) adenine ribonucleotides
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is found in nucleic acids?
A) amines
B) carboxylic acid
C) purines
D) glycerol
E) R group
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Nucleic acids, proteins, and complex carbohydrates are all produced by
A) hydrolytic reactions.
B) dehydration synthesis.
C) exchange reactions.
D) hydrogen bonding.
E) catabolic reactions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The type(s) of bond(s) produced when atoms with somewhat different electronegativities share electrons is/are
A) a nonpolar covalent bond.
B) a polar covalent bond.
C) an ionic bond.
D) a hydrogen bond.
E) both nonpolar covalent and ionic bonds.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Proteins contain both acidic and basic R groups and can, therefore, function as
A) energy storage macromolecules.
B) structural macromolecules.
C) buffers.
D) catalysts.
E) genetic material.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an atomic particle that has no electrical charge?
A) electron
B) neutron
C) element
D) proton
E) isotope
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an incorrect pairing?
A) electrolytes; anions
B) synthesis; endothermic
C) hydrolysis; hydrogen bonds
D) catabolism; exothermic
E) dehydration; anabolism
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
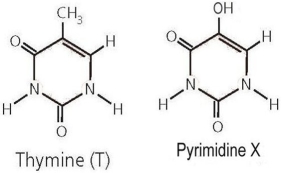 Consider the structure of thymine, shown on the left in Figure 2.3 above, and compare to the structure of pyrimidine X on the right. What would be the impact if X is incorporated into the structure of a DNA strand in place of thymine?
Consider the structure of thymine, shown on the left in Figure 2.3 above, and compare to the structure of pyrimidine X on the right. What would be the impact if X is incorporated into the structure of a DNA strand in place of thymine?
Correct Answer

verified
Where thymine has a nonpolar group, pyri...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Short Answer
An atom or molecule becomes a(n) (anion/ion/cation) when it loses an electron to a more electronegative molecule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
DNA is composed of repeating units of sugars, phosphates, and nucleic acids. This is an example of a
A) polymer.
B) monomer.
C) salt.
D) micelle.
E) lipid.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is an example of a polysaccharide?
A) glycogen
B) glucose
C) fructose
D) deoxyribose
E) sucrose
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The monomer of a nucleic acid is called a (nucleoside/nucleotide/base).
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The electron shells of atoms hold eight electrons each.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a property of water?
A) it has a high capacity for heat.
B) it is not a common reactant in metabolic reactions.
C) It is not a good solvent.
D) it is liquid in a very narrow temperature range.
E) it is a nonpolar molecule.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Describe the chemical properties of phospholipids that account for their behavior in water.
Correct Answer

verified
Phospholipids have polar phosphate "head...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Short Answer
The folding of a polypeptide into a three-dimensional shape is its (secondary/tertiary/quaternary) structure.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An acid dissociates in water to release
A) hydrogen ion(s) .
B) cation(s) .
C) hydroxyl group(s) .
D) anion(s) .
E) both anions and hydrogen ions.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Organisms use carbohydrates in all of the following ways EXCEPT
A) as a component of cell walls.
B) as a long-term energy source.
C) as a short-term energy source.
D) to keep membranes flexible at low temperatures.
E) as a building block of DNA and RNA molecules.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 76
Related Exams