A) 27 N
B) 15 N
C) 13 N
D) 17 N
E) 19 N
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A bumper car is moving at constant velocity when another bumper car starts to push on it with a constant force at an angle of 60 degrees with respect to the first car's initial velocity. The second bumper car continues pushing in exactly that direction for some time. What is most likely to happen is that
A) the first car will stop moving.
B) the first car will move in the direction of the force.
C) the first car's velocity will increase in magnitude but not change direction.
D) the first car's velocity will gradually change direction more and more toward that of the force while increasing in magnitude.
E) the first car's velocity will gradually change direction more and more toward that of the force while decreasing in magnitude.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
An astronaut who weighs 800 N on the surface of the Earth lifts off from planet Zuton in a space ship. The free-fall acceleration on Zuton is 3.0 m/s2 (down) . At the moment of liftoff the acceleration of the space ship is 0.50 m/s2 (up) . What is the magnitude of the force of the space ship on the astronaut?
A) 41 N
B) 0.29 kN
C) 0.24 kN
D) 0.20 kN
E) 0.37 kN
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the surface and the larger block is 0.25, and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the surface and the smaller block is 0.40. If F = 22 N and M = 1.0 kg in the figure, what is the magnitude of the acceleration of either block? 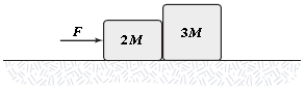
A) 1.8 m/s2
B) 2.6 m/s2
C) 1.4 m/s2
D) 2.2 m/s2
E) 3.7 m/s2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A heavy weight is supported by two cables that exert tensions of magnitude 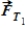 and
and 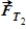 . Which statement is correct?
. Which statement is correct? 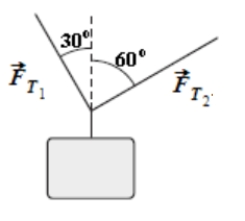
A) ![]() =
= ![]() .
.
B) ![]() =
= ![]() .
.
C) ![]() >
> ![]() .
.
D) ![]() <
< ![]() .
.
E) We need the mass of the box in order to determine the correct answer.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which type of force would be the equal and opposite force to a gravitational force?
A) gravitational
B) electromagnetic
C) strong
D) weak
E) It could be any one of the above or some combination of them.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the only forces acting on a 2.0-kg mass are 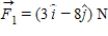 , and
, and 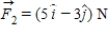 , what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the particle?
, what is the magnitude of the acceleration of the particle?
A) 1.5 m/s2
B) 6.5 m/s2
C) 4.7 m/s2
D) 9.4 m/s2
E) 7.2 m/s2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The three blocks shown are released from rest and are observed to move with accelerations that have a magnitude of 1.5 m/s2. What is the magnitude of the friction force on the block that slides horizontally? Disregard any pulley mass or friction in the pulley and let M = 2.0 kg. 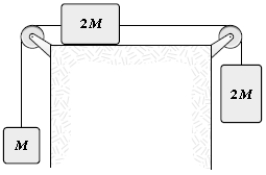
A) 6.0 N
B) 5.1 N
C) 5.5 N
D) 4.6 N
E) 3.7 N
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two blocks are accelerated across a horizontal frictionless surface as shown. Frictional forces keep the two blocks from sliding relative to each other, and the two move with the same acceleration. If F = 1.2 N and M = 1.0 kg, what is the horizontal component (frictional force) of the force of the small block on the large block? 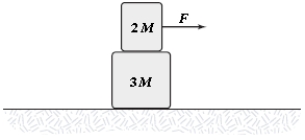
A) 0.48 N to the right
B) 0.72 N to the right
C) 0.72 N to the left
D) 0.48 N to the left
E) 0.65 N to the left
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If P = 6.0 N, what is the magnitude of the force exerted on block 1 by block 2? 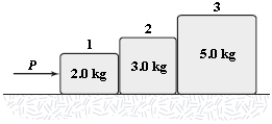
A) 6.4 N
B) 5.6 N
C) 4.8 N
D) 7.2 N
E) 8.4 N
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In the figure, if the tension in string 1 is 34 N and the tension in string 2 is 24 N, what is the mass of the object shown? 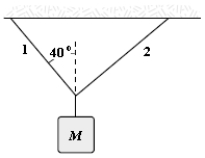
A) 7.3 kg
B) 5.5 kg
C) 1.8 kg
D) 3.7 kg
E) 4.5 kg
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two people, each of 70 kg mass, are riding in an elevator. One is standing on the floor. The other is hanging on a rope suspended from the ceiling. Compare the force 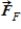 the floor exerts on the first person to the force
the floor exerts on the first person to the force 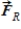 the rope exerts on the second person. Which statement is correct?
the rope exerts on the second person. Which statement is correct?
A) They are equal and opposite in direction.
B) They are equal and have the same direction.
C) ![]() is greater than
is greater than ![]() , but they have the same direction.
, but they have the same direction.
D) ![]() is greater than
is greater than ![]() , but they have opposite directions.
, but they have opposite directions.
E) ![]() is less than
is less than ![]() , but they have the same direction.
, but they have the same direction.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When the vector sum of three co-planar forces, 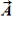 ,
, 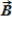 , and
, and 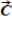 , is parallel to
, is parallel to 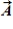 , we can conclude that
, we can conclude that 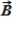 and
and 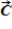
A) must sum to zero.
B) must be equal and opposite.
C) must have equal and opposite components perpendicular to ![]() .
.
D) must have equal and opposite components parallel to ![]() .
.
E) must have equal and opposite components parallel and perpendicular to ![]() .
.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The block shown is pulled across the horizontal surface at a constant speed by the force shown. If M = 5.0 kg, F = 14 N and θ = 35°, what is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface? 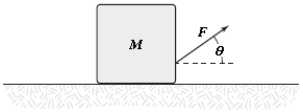
A) 0.44
B) 0.33
C) 0.38
D) 0.28
E) 0.17
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2.30-kg mass is suspended from the ceiling and a 1.70-kg mass is suspended from the 2.30-kg mass, as shown. The tensions in the strings are labeled 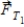 and
and 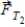 .
.
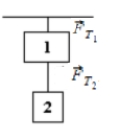
Use this exhibit to answer the following question(s) .
- A hand exerts an upward force of 6.70 N on the 1.70-kg mass. The magnitudes of the tensions are
Use this exhibit to answer the following question(s) .
- A hand exerts an upward force of 6.70 N on the 1.70-kg mass. The magnitudes of the tensions are
A) ![]() = 15.8 N;
= 15.8 N; ![]() = 10.0 N.
= 10.0 N.
B) ![]() = 15.8 N;
= 15.8 N; ![]() = 16.7 N.
= 16.7 N.
C) ![]() = 22.5 N;
= 22.5 N; ![]() = 10.0 N.
= 10.0 N.
D) ![]() = 22.5 N;
= 22.5 N; ![]() = 16.7 N.
= 16.7 N.
E) ![]() = 32.5 N;
= 32.5 N; ![]() = 10.0 N.
= 10.0 N.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two blocks connected by a string are pulled across a horizontal surface by a force applied to one of the blocks, as shown. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the blocks and the surface is 0.25. If each block has an acceleration of 2.0 m/s2 to the right, what is the magnitude F of the applied force? 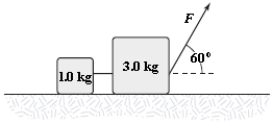
A) 25 N
B) 18 N
C) 11 N
D) 14 N
E) 7.0 N
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If F = 4.0 N and m = 2.0 kg, what is the magnitude a of the acceleration for the block shown below? The surface is frictionless. 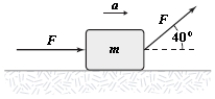
A) 5.3 m/s2
B) 4.4 m/s2
C) 3.5 m/s2
D) 6.2 m/s2
E) 8.4 m/s2
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The horizontal surface on which the objects slide is frictionless. If M = 2.0 kg, the tension in string 1 is 12 N. Determine F. 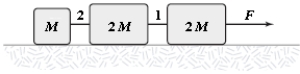
A) 25 N
B) 20 N
C) 30 N
D) 35 N
E) 40 N
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A 2.0-kg object has a velocity of 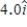 m/s at t = 0. A constant resultant force of
m/s at t = 0. A constant resultant force of  then acts on the object for 3.0 s. What is the magnitude of the object's velocity at the end of the 3.0-s interval?
then acts on the object for 3.0 s. What is the magnitude of the object's velocity at the end of the 3.0-s interval?
A) 9.2 m/s
B) 6.3 m/s
C) 8.2 m/s
D) 7.2 m/s
E) 7.7 m/s
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
You hold a tennis racket in your hand. On top of the racket you have balanced a ball. Which statement is true?
A) The force of your hand on the racket and the force of the ball on the racket are equal and opposite.
B) The force of the racket on your hand and the force of the ball on the racket are equal and opposite.
C) The force of your hand on the racket and the force of the racket on the ball are equal and opposite.
D) The force of the racket on your hand and the force of the racket on the ball are equal and opposite.
E) The force of your hand on the racket and the force of the racket on your hand are equal and opposite.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 103
Related Exams