A) allocative efficiency.
B) productive efficiency.
C) the consumer surplus.
D) the producer surplus.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
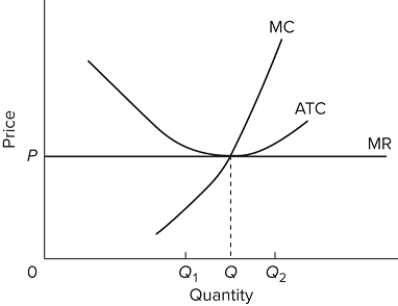 The diagram portrays
The diagram portrays
A) a competitive firm that should shut down in the short run.
B) the equilibrium position of a competitive firm in the long run.
C) a competitive firm that is realizing an economic profit.
D) the loss-minimizing position of a competitive firm in the short run.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following outcomes is consistent with a purely competitive market in long-run equilibrium?
A) Combined consumer and producer surplus will be maximized.
B) P = MC = lowest AVC.
C) The minimum willingness to pay equals the maximum acceptable price.
D) We would expect all of these to occur in the long run in a purely competitive market.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
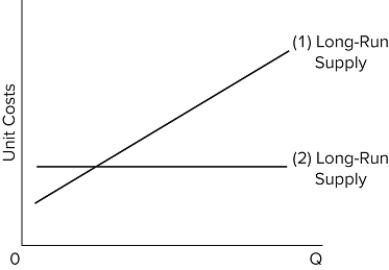 Line (1) in the diagram reflects the long-run supply curve for
Line (1) in the diagram reflects the long-run supply curve for
A) a constant-cost industry.
B) a decreasing-cost industry.
C) an increasing-cost industry.
D) a technologically progressive industry.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
It is possible for a competitive firm that is maximizing profits in the short run to make its profits even bigger in the long run by expanding its plant, assuming that the product price stays the same.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
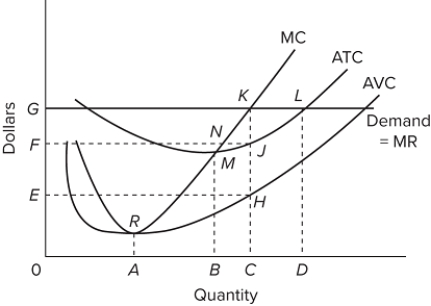 If the firm shown in this graph is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output in the short run, then it is achieving productive and allocative efficiency.
If the firm shown in this graph is producing at the profit-maximizing level of output in the short run, then it is achieving productive and allocative efficiency.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An underallocation of resources is occurring in a purely competitive industry whenever the price of the product is greater than marginal cost.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
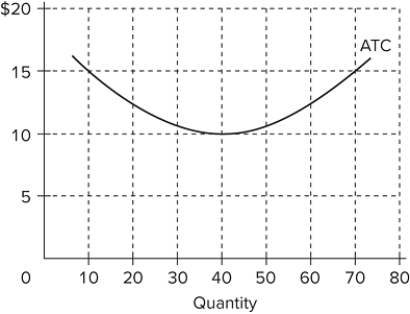 The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total cost
The diagram shows the average total cost curve for a purely competitive firm. At the long-run equilibrium level of output, this firm's total cost
A) is $10.
B) is $40.
C) is $400.
D) cannot be determined from the information provided.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is not a factor that automatically pushes firms in pure competition to earn only normal profits in the long run?
A) entry of new firms
B) exit of some firms
C) changes in the firms' plant size
D) changes in the market demand
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Assume a purely competitive constant-cost industry is initially in long-run equilibrium, producing 9 million units at a market price of $18.00. Suppose that an increase in consumer demand occurs. After all economic adjustments have been completed, which output and price combination is most likely to occur?
A) 9.5 units at a price of $19.25.
B) 10 units at a price of $18.00.
C) 9 units at a price of $20.00.
D) 8 units at a price of $18.00.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 241 - 250 of 250
Related Exams