A) 2.0 M
B) (2.0) 1/3 M
C) (2.0) - 1/3 M
D) 8.0 M
E) (8.0) - 1 M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Inert helium gas was injected into a reaction vessel of fixed volume containing an equilibrium mixture of 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) ![Inert helium gas was injected into a reaction vessel of fixed volume containing an equilibrium mixture of 2 SO₂ (g) + O₂(g) 2 SO<sub>3</sub>(g) . The pressure was increased from 1.0 atm to 2.0 atm by the adding helium. Which of the following statements describes the new equilibrium system? A) [SO<sub>3</sub>] increases B) [SO<sub>2</sub>] increases C) [SO<sub>3</sub>] decreases D) [O<sub>2</sub>] increases E) [SO<sub>3</sub>], [SO<sub>2</sub>], and [O<sub>2</sub>] remain unchanged](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TBX8714/11ebff50_c8b2_32b7_8da6_91435ed1c22b_TBX8714_11.jpg) 2 SO3(g) . The pressure was increased from 1.0 atm to 2.0 atm by the adding helium. Which of the following statements describes the new equilibrium system?
2 SO3(g) . The pressure was increased from 1.0 atm to 2.0 atm by the adding helium. Which of the following statements describes the new equilibrium system?
A) [SO3] increases
B) [SO2] increases
C) [SO3] decreases
D) [O2] increases
E) [SO3], [SO2], and [O2] remain unchanged
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At 700 C, the equilibrium constant ( K c ) for the reaction
N₂(g) + 3 H₂ (g) 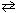 2 NH₃(g) is 2.37 10 - 3 .
If 0.683 mol of N₂, 8.80 mol of H₂ and 0.744 mole of NH₃are mixed in a 1.00 L container at 700 C:
2 NH₃(g) is 2.37 10 - 3 .
If 0.683 mol of N₂, 8.80 mol of H₂ and 0.744 mole of NH₃are mixed in a 1.00 L container at 700 C:
A) the value of Q is unknown.
B) the value of Q is greater than K c.
C) the value of Q is equal to K c.
D) the reaction is at equilibrium.
E) the value of Q is less than K c.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider solving for the molar solubility of a 3:2 electrolyte such as Mg3(PO4) 2. What solubility product expression listed below would be suitable for solving for "x" which could then be related to the solubility of Mg3(PO4) 2?
A) K sp = x5
B) K sp = 4x3
C) K sp = 6x5
D) K sp = 5x5
E) K sp = 108x5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Mg(OH) 2 ( K sp = 8.9×10 - 12) is precipitated by the addition of strong base to a 0.10 M solution of MgCl2. At what [OH - ] will Mg(OH) 2 begin to precipitate?
A) 1.0 M
B) 0.10 M
C) 9.4×10 - 6 M
D) 2.1×10 - 4 M
E) 8.9×10 - 12 M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given:
2 Cl₂ (g) + 2 H₂ O (g) 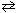 4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) K c (480 C) = 0.0752 What would be the equilibrium constant, K c , for the equation that follows?
Cl₂ (g) + H₂ O (g)
4 HCl (g) + O₂(g) K c (480 C) = 0.0752 What would be the equilibrium constant, K c , for the equation that follows?
Cl₂ (g) + H₂ O (g) 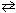 2 HCl (g) + 1 / 2 O₂(g) K c (480 C) = ??
2 HCl (g) + 1 / 2 O₂(g) K c (480 C) = ??
A) 5.66×10 - 3
B) 0.0376
C) 0.0752
D) 0.150
E) 0.274
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At a certain temperature, for the reaction NH ₄Cl (s) 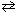 NH₃(g) + HCl (g) , K p = 9.0.
What is the equilibrium partial pressure of NH₃?
NH₃(g) + HCl (g) , K p = 9.0.
What is the equilibrium partial pressure of NH₃?
A) 9.0 atm
B) 0.11 atm
C) 3.0 atm
D) 0.33 atm
E) 0.91 atm
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider solving for the molar solubility of a 1:3 electrolyte such as Al(OH) 3. After constructing an ICE table and writing a solubility constant expression for this process, what solubility product expression listed below would be suitable for solving for "x" which could then be directly related to the solubility of Al(OH) 3 in water?
A) K sp = 3x3
B) K sp = 27x3
C) K sp = x4
D) K sp = 3x4
E) K sp = 27x4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the reaction 2 SO₂ (g) + Cl₂ (g) 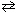 2 SO₂ Cl₂ (g) , the expression for K c is
2 SO₂ Cl₂ (g) , the expression for K c is
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A reaction vessel is charged with 1.720 atm of N₂O4 and 1.220 atm of NO₂ at 25 C. The equilibrium reaction is given in the equation below. N₂O4 (g) 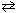 2 NO₂ (g)
After equilibrium is reached, the partial pressure of NO₂ is 0.555 atm. What is the value for the equilibrium constant, K c , of this reaction at 25 C?
2 NO₂ (g)
After equilibrium is reached, the partial pressure of NO₂ is 0.555 atm. What is the value for the equilibrium constant, K c , of this reaction at 25 C?
A) K c = 0.129
B) K c = 0.150
C) K c = 0.222
D) K c = 0.270
E) K c = 6.67
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
At 1073 K, the pressure of CO₂ is 0.236 atm when produced by the reaction:
CaCO3(s) 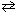 CaO (s) + CO₂ (g) The value of K c for this reaction at 1073 K is (R = 0.0821 L atm/(mol K) ) :
CaO (s) + CO₂ (g) The value of K c for this reaction at 1073 K is (R = 0.0821 L atm/(mol K) ) :
A) 0.236
B) 3.59×10 - 3
C) 2.65×10 - 5
D) 2.68×10 - 3
E) 3.55×10 - 5
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Consider the following reaction at 1200 K:
CH4 (g) + H₂ O (g) 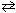 CO (g) + 3 H₂ (g) K c = 0.26 What is the pressure equilibrium constant, K p ?
CO (g) + 3 H₂ (g) K c = 0.26 What is the pressure equilibrium constant, K p ?
A) K p = 0.26; K p and K c are always equivalent.
B) K p = 2.7×10 - 5
C) K p = 1.5×10 - 3
D) K p = 6.6×102
E) K p = 2.5×103
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the solubility of PbSO4 ( K sp = 2.0×10 - 8) in a solution that contains 100.0 g of Na2SO4 in 1.00 L?
A) 1.7×10 - 4 M
B) 2.0×10 - 10 M
C) 2.4×10 - 8 M
D) 2.8×10 - 8 M
E) 2.0×10 - 8 M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For the high temperature equilibrium system, 2 H₂ O (g) 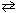 2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g) , what will be the effect on the equilibrium concentration of O₂(g) upon:
(1) adding H₂ O (g) and (2) decreasing the pressure of the system?
2 H₂ (g) + O₂(g) , what will be the effect on the equilibrium concentration of O₂(g) upon:
(1) adding H₂ O (g) and (2) decreasing the pressure of the system?
A) (1) and (2) increase the concentration of O2
B) (1) increases while (2) decreases the concentration of O2
C) (1) decreases while (2) increases the concentration of O2
D) (1) and (2) decrease the concentration of O2
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Exhibit 14-6 Consider the reaction at equilibrium below and its corresponding equilibrium constant to answer the following question(s) . 2 NO₂ (g) 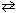 2 NO (g) + O₂(g) K p = 4.48*10- 13 A pressure of 0.45 atm of NO₂ is introduced into a container and allowed to come to equilibrium. Complete the ICE equilibrium table shown below to get started. Partial pressure S2NO₂ 2 NO O₂Initial 0.45 M Change At equilibrium
-Refer to Exhibit 14-6. Upon constructing an ICE table, what expression would be obtained that represents the equilibrium partial pressure of NO₂ as it reaches equilibrium?
2 NO (g) + O₂(g) K p = 4.48*10- 13 A pressure of 0.45 atm of NO₂ is introduced into a container and allowed to come to equilibrium. Complete the ICE equilibrium table shown below to get started. Partial pressure S2NO₂ 2 NO O₂Initial 0.45 M Change At equilibrium
-Refer to Exhibit 14-6. Upon constructing an ICE table, what expression would be obtained that represents the equilibrium partial pressure of NO₂ as it reaches equilibrium?
A) equilibrium PNO2 = 0.45 atm - x
B) equilibrium PNO2 = 0.45 atm + x
C) equilibrium PNO2 = 0.45 atm - 2x
D) equilibrium PNO2 = 0.45 atm + 2x
E) equilibrium PNO2 = 0.45 atm + 1/2 x
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the molar solubility of Ag2SO4 in 0.11 M Na2SO4? K sp(Ag2SO4) = 1.5×10 - 5
A) [Ag2SO4] = 1.2×10 - 9 M
B) [Ag2SO4] = 3.4×10 - 5 M
C) [Ag2SO4] = 6.8×10 - 5 M
D) [Ag2SO4] = 5.8×10 - 3 M
E) [Ag2SO4] = 8.3×10 - 3 M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the molar solubility of Al(OH) 3, given K sp[Al(OH) 3] = 3×10 - 34?
A) [Al(OH) 3] = 2.2×10 - 12 M
B) [Al(OH) 3] = 1.8×10 - 9 M
C) [Al(OH) 3] = 3.2×10 - 9 M
D) [Al(OH) 3] = 4.2×10 - 9 M
E) [Al(OH) 3] = 9.5×10 - 9 M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the equilibrium constant expression for the following unbalanced equation at equilibrium?
(Pay careful attention to the phase indicators!) Na2 O₂(s) + CO₂ (g) 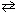 Na2 CO3(s) + O₂(g)
Na2 CO3(s) + O₂(g)
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
E) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One liter of solution is made containing 10 - 4 moles of Mn2+ and 10 - 5 moles of Fe2+. The [OH - ] is adjusted to 1.82×10 - 4 M . Which of the following statements is true, given K sp [Mn(OH) 2] = 4.5×10 - 14 and K sp [Fe(OH) 2] = 2.0×10 - 15?
A) Both Mn and Fe will precipitate as hydroxides.
B) Only Fe2+ will precipitate.
C) Only Mn2+ will precipitate.
D) Neither will precipitate.
E) Need more information to draw a conclusion.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the concentration of Ag+ ions in a saturated solution of Ag2CrO4 in water? K sp = 9.0×10 - 12 for Ag2CrO4.
A) 2.1×10 - 4 M
B) 1.0 M
C) 2.6×10 - 4 M
D) 1.3×10 - 4 M
E) 3.0×10 - 6 M
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 60 of 212
Related Exams