Correct Answer

verified
Changes in chromosome number that involv...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
True/False
The risk of having a child with Down syndrome due to a chromosomal translocation is independent of maternal age.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Using fetal DNA from the mother's blood for prenatal testing is a noninvasive procedure.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
There are ____________________ chromosomes in a human tetraploid cell.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
The long arm of a chromosome is called the ____________________ arm.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Essay
Explain how to determine if a nondisjunction occurred during meiosis I or meiosis II and what the genetic consequences are for the resulting fertilized gametes.
Correct Answer

verified
If nondisjunction occurs in meiosis I,al...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Essay
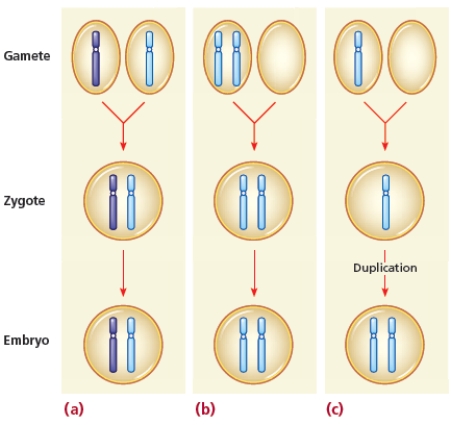 -Describe normal embryo formation and two mechanisms of nondisjunction represented in the figure and identify the consequences of these chromosomal anomalies.
-Describe normal embryo formation and two mechanisms of nondisjunction represented in the figure and identify the consequences of these chromosomal anomalies.
Correct Answer

verified
The figure represents uniparental disomy...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Studies of sex chromosome aneuploidy reveal that ____ necessary for survival.
A) the X chromosome is not
B) the Y chromosome is not
C) two copies of the X chromosome are
D) two copies of the Y chromosome are
E) at least one copy of both the X and the Y chromosome is
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Early investigators associated the tendency to violent criminal behavior with the ____________________ karyotype,but there is no evidence of a direct link between the two.
Correct Answer

verified
XYY
XYY sy...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
XYY sy...
View Answer
Short Answer
The karyotype designation for a female with X chromosome trisomy is ____________________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Autism,Alzheimer disease,Parkinson's disease,and schizophrenia are all associated with ____.
A) copy number variants
B) fragile sites
C) inversions
D) deletions
E) translocations
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Free fetal DNA (ffDNA)originates from the breakdown of fetal cells and their nuclei in the ____________________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most triploid zygotes probably arise from ____.
A) incomplete meiosis I
B) incomplete meiosis II
C) incomplete mitosis
D) nondisjunction
E) dispermy
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Almost all chromosomally abnormal embryos and fetuses are ____________________ as pregnancy progresses.
Correct Answer

verified
eliminated...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Multiple Choice
Regions at the ends of chromosomes that prevent chromosomes from sticking to each other are called ____.
A) satellites
B) telomeres
C) centromeres
D) q zones
E) p zones
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a(n) ____ translocation,two nonhomologous chromosomes exchange parts and no genetic information is gained or lost from the cell in the exchange.
A) cri du chat
B) XXY
C) copy number
D) Robertsonian
E) reciprocal
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
One type of polyploidy is ____.
A) aneuploidy
B) trisomy
C) triploidy
D) deletion
E) translocation
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Short Answer
Changes in the number of copies of chromosomal DNA segments and the genes they contain are called ____________________.
Correct Answer

verified
copy numbe...View Answer
Show Answer
Correct Answer
verified
View Answer
Short Answer
Amniocentesis collects cells from the fluid surrounding the fetus in order to prepare a(n)____________________.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Polyploidy is characterized by ____.
A) the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis
B) a condition in which one chromosome is present in three copies
C) a condition in which one member of a chromosomal pair is missing
D) a chromosomal number that is not an exact multiple of the haploid set
E) a chromosomal number that is a multiple of the normal haploid chromosomal set
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 60
Related Exams