A) the change in total cost resulting from adding one more unit of a factor.
B) the change in the quantity of a factor divided by the change in total cost.
C) MP multiplied by the price of the output.
D) less than the factor price after the first unit of factor.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question(s) : Monopsony
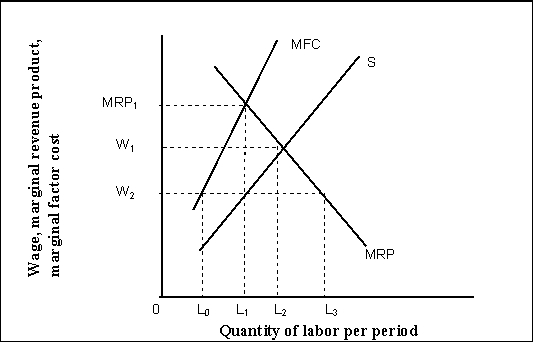 -(Exhibit: Monopsony) Which of the following is (are) true?
-(Exhibit: Monopsony) Which of the following is (are) true?
A) Given perfect competition in the factor market, the price of a factor is equal to the MFC.
B) Given imperfect competition in the factor market, the price of a factor is less than the MFC.
C) Given perfect competition in the product market, MRP = MP times the price of output, and given imperfect competition in the product market, MRP = MP times MR, which is less than MP times price.
D) All of the above are true.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm that has monopoly power in the supply of a factor makes choices in same manner as any other monopoly firm by selling where _______ and selecting a price determined by the _______ curve.
A) MR = P; demand
B) MR = MC; supply
C) MR = MC; demand
D) MRP = MFC; supply
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The marginal factor cost curve for a monopsonist is:
A) vertical.
B) horizontal.
C) negatively sloped.
D) positively sloped.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A firm that is a monopsony in its market for a factor of production:
A) faces a horizontal supply curve of labor.
B) constitutes the entire market for the factor.
C) is a factor price taker.
D) can't change the quantity of the factor it hires.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question(s) : Wage-Employment Model in a Bilateral Monopoly Market
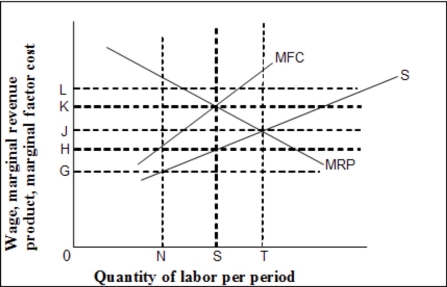 -(Exhibit: Wage-Employment Model in a Bilateral Monopoly Market) If this diagram portrayed a bilateral monopoly model, the wage rate would be:
-(Exhibit: Wage-Employment Model in a Bilateral Monopoly Market) If this diagram portrayed a bilateral monopoly model, the wage rate would be:
A) 0K.
B) 0J.
C) 0H.
D) indeterminate.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question(s) : Minimum Wage and Monopsony
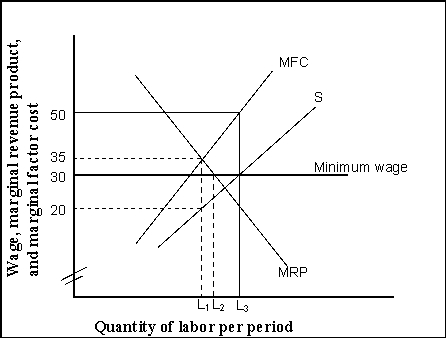 -(Exhibit: Minimum Wage and Monopsony) In the absence of a minimum wage, the monopsony firm in the exhibit would maximize profits by hiring _______ units of labor per period, and setting the wage at _______ .
-(Exhibit: Minimum Wage and Monopsony) In the absence of a minimum wage, the monopsony firm in the exhibit would maximize profits by hiring _______ units of labor per period, and setting the wage at _______ .
A) L₁; $35
B) L₁; $20
C) L₂; $30
D) L₃; $50
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Increasing the demand for union-made products is likely to cause the wage of union workers to ________ and the quantity of labor employed in unionized industries to ________, all other things unchanged.
A) increase; increase
B) increase; decrease
C) decrease; increase
D) decrease; decrease
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A union shop is a firm that can hire and retain union as well as nonunion workers, and nonunion workers do not have to meet union requirements.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is true, assuming that a firm is a price taker in the labor market?
A) The firm faces a demand curve for labor that is horizontal.
B) The firm faces a supply curve of labor that is horizontal.
C) The firm faces a supply curve of labor that is the MRP of labor.
D) The firm faces a demand curve for labor that is vertical.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The considerable differences in the wages of minor league athletes and major league athletes since 1977 is most likely due to:
A) chance or luck.
B) work effort.
C) differences in their respective marginal revenue products.
D) the strength of the major league union.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Closed-shop arrangements:
A) constitute the greatest percentage of unions.
B) are increasing in number.
C) have been declared illegal in the United States.
D) are generally found in states with right-to-work laws.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Colleges and universities in small towns generally pay part-time instructors ________ they pay full-time instructors per credit-hour.
A) more than
B) less than
C) about the same as
D) about 10 percent of what
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A monopsony is a market characterized by:
A) one seller of an output.
B) one buyer of an input.
C) two buyers of an input.
D) many buyers of an input.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question(s) : Labor Market
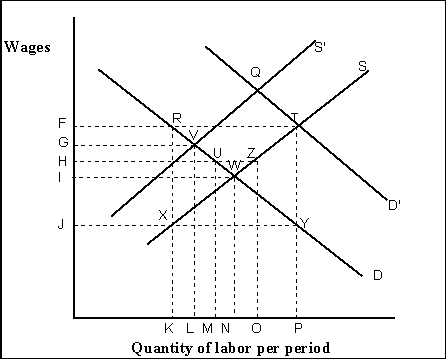 -(Exhibit: Labor Market) Given competitive market demand curve D and union members supply curve S, an increase in the demand for the union-made product will result in a:
-(Exhibit: Labor Market) Given competitive market demand curve D and union members supply curve S, an increase in the demand for the union-made product will result in a:
A) new demand curve FTD′.
B) new supply curve FTS.
C) shift in the supply curve to S′.
D) shift in the demand curve to D′.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question(s) : Wage-Employment Model in Perfectly Competitive and Monopsony Factor Markets
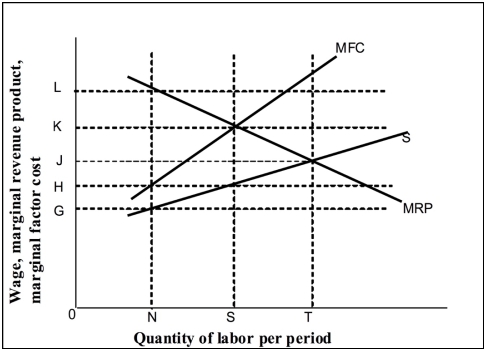 -(Exhibit: Wage-Employment Model in Perfectly Competitive and Monopsony Factor Markets) If this diagram portrayed a perfectly competitive market, the equilibrium-wage rate would be:
-(Exhibit: Wage-Employment Model in Perfectly Competitive and Monopsony Factor Markets) If this diagram portrayed a perfectly competitive market, the equilibrium-wage rate would be:
A) 0H.
B) 0J.
C) 0K.
D) 0L.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question(s) : Supply and Marginal Factor Cost
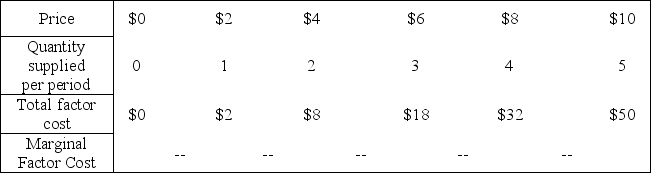 -(Exhibit: Supply and Marginal Factor Cost) If the supply curve implied in this exhibit is faced by a single firm, it would be a firm:
-(Exhibit: Supply and Marginal Factor Cost) If the supply curve implied in this exhibit is faced by a single firm, it would be a firm:
A) hiring in a perfectly competitive factor market
B) that is a price taker in the factor market.
C) that is called a monopoly seller in the factor market.
D) that is called a monopsony.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question 63-70.
Exhibit: Monopoly and Monopsony
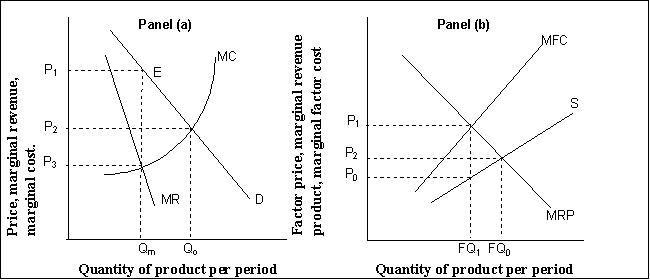 -(Exhibit: Monopoly and Monopsony) In Panel (b) , if activity is carried on at the maximizing level specified by the marginal decision rule:
-(Exhibit: Monopoly and Monopsony) In Panel (b) , if activity is carried on at the maximizing level specified by the marginal decision rule:
A) MFC < factor price.
B) MFC = factor price.
C) MFC > factor price.
D) MFC < MRP.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer question 63-70.
Exhibit: Monopoly and Monopsony
 -(Exhibit: Monopoly and Monopsony) In Panel (a) , if the quantity of production is carried to the right of point E:
-(Exhibit: Monopoly and Monopsony) In Panel (a) , if the quantity of production is carried to the right of point E:
A) MR < MC
B) MR = P
C) MR > P
D) MRP > MFC
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
To maximize profits, a perfectly competitive firm applies the marginal decision rule and thus:
A) sells where P = AVC.
B) hires factors until MP = MFC.
C) hires a factor up to the point that the extra revenue generated by the extra output of the additional unit of the factor is equal to the extra cost of hiring the additional unit of the factor.
D) hires factors until MP = MC.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 161 - 180 of 183
Related Exams