A) resource abundance.
B) the number of offspring produced each reproductive cycle.
C) chances of survivorship until sexual maturity.
D) how frequently each individual in the population reproduces.
E) the age at which reproduction ends.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
When a population reaches the stable equilibrium phase,this is considered
A) the carrying capacity of the environment.
B) logarithmic growth.
C) exponential growth.
D) the minimum number of individuals that the environment can sustain.
E) the slow growth stage.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a recent hurricane,25 individuals of the same butterfly species were blown onto a barrier island in southern Florida.During the first year,80 caterpillars hatched from eggs laid by the butterflies and only 5 individuals in the population died.What is the growth rate for the population during this period?
A) 1%
B) 3%
C) 10%
D) 30%
E) 400%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is correct about the comparison between MDCs and LDCs?
A) MDCs consume 4xs as many metals and 3xs as much paper as LDCs.
B) MDCs consume twice as much paper and 4xs as many metals as LDCs.
C) MDCs population is growing twice as fast as the population of LDCs
D) MDCs produce 10xs as much hazardous waste and consume 3xs as much paper as LDCs
E) MDCs consume 3xs as many metals and 4xs as much paper as LDCs.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following represents a Type II survivorship curve?
A) organisms that have lots of offspring but only a few survive to reproduce
B) organisms that have an equal probability of dying all age groups
C) organisms that provide parental care
D) organisms that survive for many years before they reproduce
E) organisms that have low mortality during their early years
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Honey bees have been declining at dramatic rates in the last few years.Colony collapse disorder has been linked to a virus and results in hives completely emptied of bees among both wild populations and domestic hives.Recently,scientists have suggested that infected bees may contaminate flowers that they visit and thus spread the disease.This is an example of a(n)
A) clumped distribution.
B) density-dependent factor.
C) random factor.
D) density independent factor.
E) biotic potential.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Emperor penguins defend an area around their nests.Their territory encompasses a complete circle around the nest with approximately a 0.5m radius.If each nesting penguin has this same size and shape territory,what type of distribution will these animals exhibit?
A) clumped
B) random
C) dense
D) uniform
E) independent
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the greatest problem that the human population will face if we fail to have a greater understanding of ecology and environmental science?
A) We will have a lack of understanding about the problems that the human population poses to the health of the biosphere.
B) We will have a lack of understanding about the ability of the human population to obtain additional resources from the environment.
C) We will not understand how to expand human society into currently uninhabited areas on the planet.
D) The human population will start to decline in size.
E) The human population will go extinct in the near future.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a population of 200 squirrels has a 10 percent growth rate each year,how many individuals will there be in the population after 3 years (assume that no deaths occur during this period) ?
A) approximately 250
B) approximately 275
C) approximately 300
D) approximately 350
E) approximately 400
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is an organism's biotic potential?
A) The rate at which the population grows.
B) The number of offspring that an organism produces over its entire lifespan.
C) The age at which an organism reaches sexual maturity.
D) The number of individuals in the prereproductive stage.
E) The maximum rate of population growth with unlimited resources.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the carrying capacity for the population of beetles indicated by the graph? 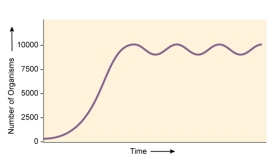
A) ~ 5,000
B) ~ 10,000
C) ~ 100,000
D) ~ 2,500
E) cannot be determined from the graph
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following represents replacement reproduction?
A) a couple has only one child
B) a couple has no children but each has two siblings
C) each couple has only two children
D) a government policy that limits the number of children per family
E) a couple with four children
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In which of the following areas is human population growth the lowest?
A) Africa
B) North America
C) Australia
D) Europe
E) South America
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Schools of parrot fish tend to remain within close proximity to coral reefs for protection from predators and for easy access to food sources.What type of distribution does this represent?
A) clumped
B) random
C) dense
D) uniform
E) independent
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which field of biology studies all aspects of biodiversity?
A) conservation biology
B) histology
C) geology
D) entomology
E) environmental science
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In European countries such as Italy,people are delaying childbirth and or choosing to have only one or no children.Which of the following age structure diagrams illustrates this type of trend? 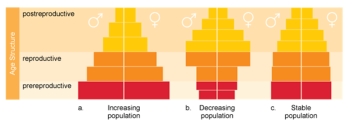
A) increasing population
B) decreasing population
C) stable population
D) This trend is not depicted in these diagrams
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
During a recent hurricane,25 individuals of the same butterfly species were blown onto a barrier island in southern Florida.Prior to this event,this species did not inhabit the island,but with the ample vegetation on the island and a lack of predators,the displaced individuals were able to survive and reproduce.When the butterflies initially arrived on the island,they did not have to compete for food or space.What type of population growth did they likely exhibit?
A) logistic
B) exponential
C) density-dependent
D) density-independent
E) logarithmic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
All of the following are true about human population growth EXCEPT
A) the majority of the world's human population live in Asia.
B) the black plague resulted in a decreased growth rate in the 1300s.
C) changes during the Industrial Revolution lead to a steep rise in the human population.
D) we will reach the Earth's carrying capacity within the next 20 years.
E) human population densities tend to be highest along the coasts.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 41 - 58 of 58
Related Exams