A) binding price ceiling.
B) binding price floor.
C) nonbinding price ceiling.
D) nonbinding price floor.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Setting the maximum legal price above the market price will cause
A) a shortage to develop.
B) the market to reach an equilibrium outcome.
C) quantity supplied to exceed quantity demanded.
D) market inefficiencies.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement about price controls is most correct?
A) Price controls often hurt the people they are designed to help.
B) Price controls always help the people they are designed to help.
C) Price controls have minimal adverse effects.
D) Price controls make economic sense even if they have adverse effects.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which statement about price ceilings is correct?
A) Whether a price ceiling is placed below or above the equilibrium price,it will always cause deadweight loss.
B) A price ceiling will only cause deadweight loss if it is placed above the equilibrium price.
C) A price ceiling will only cause deadweight loss if it is placed below the equilibrium price.
D) Whether a price ceiling is placed below or above the equilibrium price,it will always cause a shortage of the good.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If price controls are imposed,gains from trade,including consumer and producer surplus,are likely to increase.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Housing vouchers are a better option than rent controls when a government is attempting to make housing affordable for the poor.The reason is that the housing voucher entitles the tenant to:
A) live in a rent-controlled apartment.
B) free maintenance of their apartment.
C) a certain dollar amount off the rent of any apartment they choose.
D) live in a luxury apartment of their choice.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The price controls of the early 1970s caused:
A) lead to be removed from gasoline.
B) the disappearance of the full-service gas station.
C) gas stations to stay open for more hours.
D) an excess supply of gasoline.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The blat economy described in the text results when price controls are:
A) extensive and cause chronic shortages in the economy.
B) extensive but the causes of shortages in the economy are only temporary.
C) short-lasting but cause chronic shortages in the economy.
D) short-lasting and cause only temporary shortages in the economy.
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
A price ceiling is a legal maximum on the price of the good or service.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The quantity traded with a binding price ceiling is lower than the quantity traded without a price ceiling,which means that price ceilings create lost gains from trade.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these statements explains why price ceilings result in lost gains from trade?
A) Buyers and sellers want to trade,but the threat of fines or jail time prevents them from doing so.
B) Sellers want to trade,but buyers prefer the lower prices.
C) Buyers want to trade,but sellers are indifferent at the lower prices.
D) Neither buyers nor sellers want to trade subject to a price ceiling resulting in lost gains from trade.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Minimum wage laws are an example of price floors.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
How can sellers increase profits when they face a price ceiling?
A) charge a higher price for the good
B) charge a lower price for the good to undercut rival sellers
C) produce and sell more output
D) reduce the quality of the product and provide less customer service
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Once one accounts for time costs and bribes,it may be more expensive to make purchases at the government-controlled price than at the free-market price.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Prices ceilings misallocate resources because with them resources are not necessarily allocated to their highest-valued use.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Figure: Costs of Price Ceilings 2 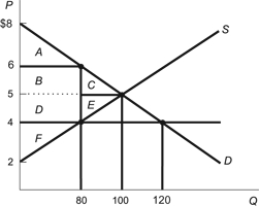 -(Figure: Costs of Price Ceilings 2) Refer to the figure.What is the dollar amount of lost producer surplus after the price ceiling of $4 has been implemented?
-(Figure: Costs of Price Ceilings 2) Refer to the figure.What is the dollar amount of lost producer surplus after the price ceiling of $4 has been implemented?
A) $90
B) $10
C) $160
D) $80
F) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A major hurricane damages many oil refineries,which increases the market price of gasoline from $3.50 to $5 per gallon.The Attorney General threatens legal action against gas station owners who raise prices above pre-hurricane levels,causing gas station owners to reluctantly sell gas for $3.50 per gallon.At $3.50 per gallon,shortages cause buyers to wait in line for 2 hours.If the average purchase is 15 gallons and buyers value their time at $20 an hour,is the Attorney General helping?
A) No,paying $92.50 at $3.50 per gallon is more expensive than $75 at $5.00 per gallon.
B) Yes,paying $52.50 at $3.50 is cheaper than $75 at $5.00 per gallon.
C) Yes,gas is cheaper at $3.50 per gallon because the waiting costs keep gas prices low.
D) No,$5.00 per gallon would insure that buyers could always buy as much as they want.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
If a price floor is above the equilibrium price it will have no effect in the market.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Rent controls are:
A) an efficient and equitable way to help the poor.
B) inefficient,but a pretty good way to solve a serious social problem.
C) an inefficient way to help the poor in raising their standard of living.
D) an efficient way to allocate housing.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Use the following to answer questions
Figure: Price Ceilings and Random Allocation 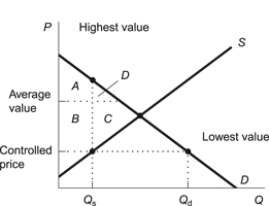 -(Figure: Price Ceilings and Random Allocation) Refer to the figure.When a controlled price is imposed and the quantity of goods is allocated randomly between the highest-valued uses and lowest-valued uses,loss due to random allocation instead of allocation to the highest-valued use is represented by area:
-(Figure: Price Ceilings and Random Allocation) Refer to the figure.When a controlled price is imposed and the quantity of goods is allocated randomly between the highest-valued uses and lowest-valued uses,loss due to random allocation instead of allocation to the highest-valued use is represented by area:
A) A.
B) B.
C) C.
D) D.
F) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 141 - 160 of 309
Related Exams