A) duplication
B) translocation
C) X-inactivation
D) loss of imprinting
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match each of the following genetic conditions with its mode of inheritance. A mode of inheritance may be used once, more than once, or not at all. -sickle cell anemia
A) autosomal recessive
B) autosomal dominant
C) X-linked recessive
D) aneuploidy
E) genomic imprinting
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is caused by the human genetic condition called progeria?
A) muscular and mental deterioration shortly after puberty
B) socially inappropriate vocal outbursts and muscular twitches
C) premature aging that typically leads to death in the early teenage years
D) pattern baldness as early as age 20
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose you are a genetic counsellor, and a man and woman come to you with concerns that if they have a child together, it could have hemophilia. Also suppose that the woman has an X-linked recessive form of hemophilia, but the man does NOT. Which of the following is the best advice you could give them?
A) Each of their male offspring will have hemophilia, and each of their female offspring will have a 50% chance of having hemophilia.
B) Each of their male offspring will have a 50% chance of having hemophilia; and while their female offspring should not have hemophilia, they will each have a 50% chance of being carriers.
C) None of their offspring should have hemophilia, but each of their female offspring will be carriers for hemophilia.
D) Each of their male offspring will have hemophilia; and while their female offspring should not have hemophilia, they will all be carriers.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following describes an individual who is a carrier of a genetically inherited disease?
A) The individual has the disease, and any offspring will have the disease.
B) The individual does not have the disease, but must have a parent with the disease.
C) The individual does not have the disease, but may have offspring with the disease.
D) The individual has the disease, and must have a parent with the disease.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which term refers to an individual with extra or missing copies of some of their chromosomes?
A) haploid
B) aneuploid
C) polyploid
D) euploid
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which phrase best defines what is meant by gene linkage?
A) genes that affect two different traits and that lead to a 9:3:3:1 phenotype ratio in a dihybrid cross
B) genes that do not sort independently due to their being physically near each other on the same chromosome
C) different alleles of the same gene
D) genes whose effects combine to affect a single characteristic
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
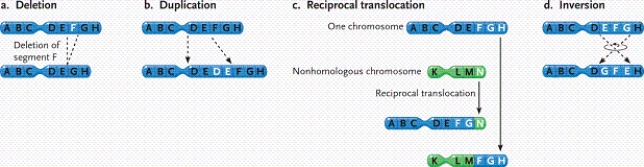 -In the figure, what type of change in the chromosomes is depicted?
-In the figure, what type of change in the chromosomes is depicted?
A) a reciprocal translocation
B) a duplication
C) an inversion
D) a deletion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that you examine a vial of 100 flies that are all offspring from a single genetic cross, and you find only red-eyed females and red-eyed males present. You allow these flies to interbreed, and in the next generation you find all the females are red-eyed, but you find both red-eyed and white-eyed males. The allele for red eye colour (Xw+) is dominant over the allele for white eye colour (Xw) . Which of the following best describes the genotypes of the original parents?
A) Xw+Xw+; XwY
B) Xw+Xw; Xw+Y
C) Xw+Xw; XwY
D) XwXw; Xw+Y
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which phrase best describes chromosomal nondisjunction?
A) failure of homologous pairs or sister chromatids to separate during meiosis
B) failure of sister chromatids to pair during mitosis
C) improper pairing of nonhomologous chromosomes during meiosis
D) failure of homologous pairs to separate during meiosis
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that in studies of genes on the same chromosome, you find the following recombination frequencies: a 40% frequency for a and b, a 30% frequency for a and c, and a 10% frequency for b and C Which phrase best describes the relationship between genes a, b, and c?
A) alternative alleles that are not physically possible because the numbers do not add up
B) linked genes that are not physically possible because the numbers do not add up
C) linked genes
D) different alleles of the same gene
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
From which studies did the discovery of sex-linked genes and the production of the first chromosome map arise?
A) from the studies of pea plants
B) from the studies of humans
C) from the studies of fruit flies
D) from the studies of corn
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What do genetic map units represent?
A) relative positions of genes with respect to each other
B) the chromosome on which a given gene is located
C) the actual DNA sequence of a gene
D) absolute physical distances between genes
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If two genes are located on different chromosomes, what percentage of the offspring should have a recombinant phenotype?
A) about 75%
B) about 50%
C) about 25%
D) about 10%
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
 -In the figure, what type of change in the chromosomes is depicted?
-In the figure, what type of change in the chromosomes is depicted?
A) an inversion
B) a deletion
C) a reciprocal translocation
D) a duplication
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose that you examine a vial of 100 flies that are all offspring from a single genetic cross. Suppose also that you see that all the females present are red-eyed and all the males present are white-eyed. The allele for red eye colour (Xw+) is dominant over the allele for white eye colour (Xw) . Which of the following describes the genotypes of the parents?
A) Xw+Xw; XwY
B) XwXw; Xw+Y
C) Xw+Xw+; XwY
D) Xw+Xw; Xw+Y
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Most hospitals routinely test all newborns for an autosomal recessive disorder in which an enzyme in amino acid metabolism is NOT produced. In this disorder, lack of the enzyme leads to a buildup of compounds that damage brain tissue, possibly leading to mental retardation, unless a restricted diet is followed. What is the name of this disorder?
A) Duchenne muscular dystrophy
B) achondroplasia
C) sickle cell anemia
D) phenylketonuria
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the name of the human disorder in which a deletion from chromosome 5 typically leads to severe mental retardation and a malformed larynx?
A) triple-X syndrome
B) cri-du-chat
C) Down syndrome
D) Turner syndrome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following processes is most likely responsible for many mammals having multiple hemoglobin genes?
A) a reciprocal translocation
B) a duplication
C) an inversion
D) a deletion
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Match each of the following genetic conditions with its mode of inheritance. A mode of inheritance may be used once, more than once, or not at all. -Down syndrome
A) autosomal recessive
B) autosomal dominant
C) X-linked recessive
D) aneuploidy
E) genomic imprinting
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 21 - 40 of 79
Related Exams