A) anticline
B) syncline
C) monocline
D) gneiss dome
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of metamorphism would occur in this setting? 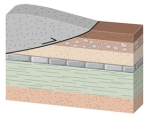
A) regional metamorphism
B) contact metamorphism
C) extension
D) normal faulting
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of these conditions could form rocks that are partly metamorphic and partly igneous? 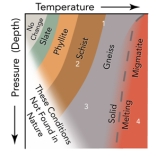
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In what direction were the rocks in the center of this cross section shortened? 
A) in a vertical direction
B) in a horizontal direction
C) they were not shortened,they were pulled apart
D) there is no way to tell
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following characterizes a continental rift?
A) contact metamorphism near magma chambers
B) normal faults
C) tension
D) metamorphism associated with shearing
E) all of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of structure is shown in this figure? 
A) thrust fault
B) anticline
C) syncline
D) monocline
E) basin
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In what environments does high pressure/low temperature metamorphism occur?
A) near magma but at shallow levels
B) near magma but at deep levels
C) under normal conditions of burial and heating
D) in a subduction zone or accretionary prism
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of fault is shown in this figure? 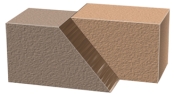
A) dip-slip fault
B) normal fault
C) strike-slip fault
D) reverse fault
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What kind of structure is shown in this image? 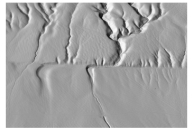
A) monocline
B) strike-slip fault
C) asymmetric fold
D) subduction zone
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What structural and metamorphic features form in a fold and thrust belt?
A) anticlines and synclines related to movement of thrust sheets over bends in thrust faults
B) cleavage
C) a predominance of normal faults
D) all of these
E) a and b only
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
This rock is not shiny and has a well-developed cleavage that cuts across bedding.What is the correct name for this rock? 
A) schist
B) quartzite
C) slate
D) gneiss
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of structure is shown in this photograph? 
A) joint
B) cleavage
C) fault
D) anticline
E) syncline
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Under what conditions was this rock likely deformed? 
A) relatively shallow
B) brittle conditions
C) conditions that favored fracturing
D) hot and deep conditions
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of stress formed the structure shown in this figure? 
A) compression
B) tension
C) shear
D) none of these because no fracture was formed
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is a valid statement about how rocks respond to stress?
A) If the stress is very high,the rock will be unchanged.
B) Stress can cause a rock to be displaced,but not rotated.
C) If a rock has strained,then it has changed its size or shape.
D) A rock can be displaced or strained but not both at the same time.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If the view is looking north,which of the following correctly indicates which rocks are higher in metamorphic grade in the following image? 
A) the banded rocks to the east
B) the rocks in the grassy area and southern hill
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of feature is shown in this photograph? 
A) anticline
B) columnar joints
C) scratch marks along a fault
D) folded metamorphic rocks
E) all of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In what site on this figure would you expect high pressure/low temperature metamorphism? 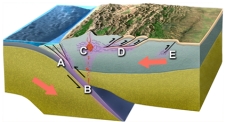
A) A and B
B) B and C
C) C and D
D) D and E
E) none of these
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What type of deformation is shown in this photograph? 
A) displacement
B) rotation
C) internal strain of the rock
D) columnar joints
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What orientation of stresses is the simplest explanation for the structure shown in this figure? 
A) equal amounts of confining pressure
B) tension from upper left to lower right
C) shearing in a vertical direction
D) shearing in a horizontal direction
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 101 - 120 of 120
Related Exams