A) When the population µ is known
B) When the population deals with two samples
C) When the population standard deviation is known
D) When the population standard deviation is unknown
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Cultural Diversity Task Force sponsored six events last year (e.g. ,Awareness Luncheon) and six events with the same names this year.To see how well the attendance last year correlated with attendance this year,the chairperson ranked the number of people attending each event during each of the two years and calculated a correlation.The chairperson used the Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient 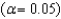 to determine if attendance this year at these events was greater than last year (a positive correlation) .The correlation would have to be bigger than _______ to be "significant."
to determine if attendance this year at these events was greater than last year (a positive correlation) .The correlation would have to be bigger than _______ to be "significant."
A) 0.886
B) 0.829
C) 0.645
D) 0.643
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following assumptions is common to both the z-test and the one-sample t-test?
A) Alpha is selected to be 0.01.
B) The raw score population forms a normal distribution,and the population mean and standard deviation are known.
C) The standard deviation of the raw score population is estimated by ![]() .
.
D) There is one random sample of interval or ratio scores.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is the formula for the 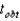 in a single-sample t-test?
in a single-sample t-test?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following is one of the assumptions of a one-sample t-test?
A) The obtained scores are on an ordinal or interval scale.
B) The population standard deviation is estimated by computing ![]() .
.
C) The population standard deviation is known.
D) The population distribution is skewed.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The critical value for 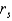 is obtained using
is obtained using
A) N,which is the total number of scores in the sample.
B) N,which is the number of pairs of scores in the sample.
C) df,which equals N 1,with N being the number of pairs of scores in the sample.
D) df,which equals N 2,with N being the number of pairs of scores in the sample.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What is the difference between Pearson's and Spearman's correlations when performing a hypothesis test?
A) The level of
B) The size of the sample
C) The assumption that the scores must be randomly selected
D) How the respective sampling distributions for each correlation are conceptualized
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Using the data given below,perform a two-tailed t-test to compare the sample mean to 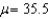 .Use
.Use 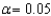 . 38 40 41 37 35 38 41
39 34 35 38 42 44 37
. 38 40 41 37 35 38 41
39 34 35 38 42 44 37
A) 2.160 < 2.601,Fail to reject ![]()
B) 2.601 > 2.160,Reject ![]()
C) -2.160 > -2.601,Reject ![]()
D) -2.601 < -2.160,Fail to reject ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Suppose you perform a two-tailed significance test on a correlation between the number of books read for enjoyment and the number of credit hours taken,using 32 participants.Your 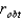 is 0.15,which is not a significant correlation coefficient.Which of the following is the correct way to report this finding?
is 0.15,which is not a significant correlation coefficient.Which of the following is the correct way to report this finding?
A) r(32) = 0.15,p > 0.05
B) r(31) = 0.15,p > 0.05
C) r(30) = 0.15,p < 0.05
D) r(30) = 0.15,p > 0.05
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For 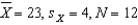 ,and
,and 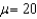 ,what is
,what is 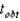 ?
?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
D
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For 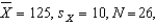 and
and 
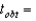 _____ and
_____ and 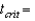 _____ for a one-tailed test with
_____ for a one-tailed test with 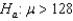 ,and
,and  .
.
A) -1.530;2.485
B) -1.530;-2.485
C) -2.485;1.530
D) -2.485;-1.530
Correct Answer

verified
A
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
What does the shape of any particular sampling distribution of a correlation coefficient depend upon?
A) df
B) µ
C) r
D) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following would increase the power of a t-test?
A) Changing from 0.05 to 0.01
B) Increasing the variability in the raw scores
C) Changing the sample size from N = 25 to N = 100
D) Changing the sample size from N = 100 to N = 25
Correct Answer

verified
C
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For 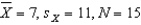 ,and
,and 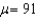 ,what is
,what is 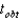 ?
?
A) ![]()
B) ![]()
C) ![]()
D) ![]()
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In a one-tailed significance test for a correlation predicted to be negative,the null hypothesis is _____ and the alternative hypothesis is _____.
A) ![]() 0;
0; ![]() < 0
< 0
B) ![]() > 0;
> 0; ![]() 0
0
C) ![]() = 0;
= 0; ![]() < 0
< 0
D) ![]() > 0;
> 0; ![]() < 0
< 0
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Unless we use the correct  from the t-distribution for the appropriate N,
from the t-distribution for the appropriate N,
A) we will fail to reject ![]() .
.
B) we will always reject ![]() .
.
C) the probability of making a Type I error will increase.
D) the probability of making a Type I error will not equal .
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A developmental psychologist interested in the development of color perception presented 20 one-month-old infants with a pair of color forms.One form had two colors and the other had one.If the infants preferred to look at the form with two colors above chance level (50%) ,they can perceive colors.The mean percentage of times the infants preferred the two-color form was 53.15 ( 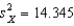 ) .What is
) .What is 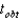 ?
?
A) 0.83
B) 0.98
C) 3.72
D) 4.39
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If we reject the null hypothesis in a significance test of correlation,we conclude that our 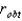
A) indicates a significant difference between the sample correlation coefficient and the true value of .
B) says there is a significant difference between the sample mean and the true population mean.
C) almost never happens when ![]() is really 0.
is really 0.
D) represents a ![]() equal to 0.
equal to 0.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If a researcher reports a one-sample t-test with df = 24,how many individuals participated in this study?
A) 24
B) 25
C) 26
D) Cannot be determined from the information given
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements about the correlation coefficient is true?
A) One should not accept that a correlation coefficient represents a relationship unless it is significant.
B) Unless a correlation coefficient is zero,it represents a relationship.
C) Positive correlation coefficients tend to be significant more often than negative ones.
D) Sampling error does not apply to the correlation coefficient.
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 1 - 20 of 57
Related Exams