A) for all distances between genes in one chromosome.
B) for distances up to about 75 map units, after which recombination frequencies become higher than expected.
C) for distances up to about 50 map units, at which point recombination frequencies become higher than expected.
D) for distances up to about 25 map units, at which point recombination frequency becomes higher than expected.
E) for distances up to about 15 map units, at which point recombination frequency becomes lower than expected.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Pairing of homologous chromosomes at metaphase of meiosis I appears to be critical for proper alignment, crossing over, and subsequent separation. This pairing is facilitated by sharing of sequence homology. If X and Y chromosomes are so different, how can they achieve the necessary pairing?
A) They share short homologies at their respective tips.
B) They use a unique sex-linked mechanism not present in other pairs.
C) They do not need to pair because they are not a homologous pair.
D) A special function of the spindle apparatus forces X and Y together.
F) B) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
If you tracked an individual X chromosome from a male to his first generation offspring, then to his second-generation offspring, what pattern would you see?
A) His X chromosome would be found only in his daughters and granddaughters.
B) His X chromosome would be found only in his sons and grandsons.
C) His X chromosome would be found only in his daughters and grandsons.
D) His X chromosome would be found only in his daughters, then in both his granddaughters and grandsons.
E) His X chromosome would be found only in his sons, then in both his granddaughters and grandsons.
G) A) and D)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
A heterozygous female harboring one mutant allele for hemophilia is called a(n) _____ for that trait.
A) carrier
B) harborer
C) homozygote
D) unaffected female
E) messenger
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Because of its unique structure, mutations in the Y chromosome:
A) are accumulated within individual Y chromosome lineages.
B) generally only affect male reproductive structure and function.
C) are helpful for mapping genes.
D) are shared only with specific regions of the X chromosome.
E) happen only rarely.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding MERRF syndrome?
A) It is an X-linked trait characterized by epilepsy and the overproduction of the lactase enzyme.
B) It is a mitochondrial disease that only appears in females, given that mitochondria are transmitted through the cytoplasm of female gametes.
C) It is a mitochondrial disease that results from a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes contained within mitochondria.
D) It is a Y-linked trait characterized by muscle weakness, which is passed from fathers to sons.
E) None of the answer options is correct.
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Given equal probabilities of the birth of a boy or girl, what is the probability that a group of three siblings includes exactly two boys? Exactly three boys? Two or more boys?
A) 1/8; 1/8; 1/4
B) 1/4; 1/4; 1/2
C) 3/8; 1/8; 1/2
D) 1/2; 1/8; 5/8
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In crosses involving linked genes, recombinant offspring result from:
A) Mendelian segregation.
B) independent assortment of alleles.
C) sex-linked inheritance.
D) a crossover.
E) Mendelian segregation and independent assortment of alleles.
G) A) and B)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Two examples of X-linked inheritance in humans are:
A) blue eyes and red hair.
B) sickle-cell anemia and alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency.
C) type II diabetes and high blood pressure.
D) red-green color blindness and hemophilia.
E) None of the answer options is correct.
G) All of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
For two genes that show independent assortment, what is the frequency of recombination?
A) 100%
B) 75%
C) 50%
D) 25%
E) 0%
G) None of the above
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Considering a rare X-linked recessive trait, which of the following statements is/are TRUE?
A) An unaffected woman whose father was affected is expected to have unaffected sons.
B) An unaffected father is expected to have unaffected daughters.
C) An affected mother is expected to have affected sons.
D) An affected father is expected to have affected daughters.
E) Both parents have to be affected in order to have affected daughters.
G) D) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
In humans and other mammals, the sex-determining region in the Y chromosome is required for male development.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
The small area near the centromere is the most likely location for recombination between two homologous chromosomes.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding Y-linked traits?
A) A female can transmit a Y-linked trait as a result of crossing over between homologous portions of the X and Y chromosomes.
B) Only males will demonstrate a Y-linked trait.
C) Only about half of all the male progeny from a male demonstrating a Y-linked trait will also have that trait.
D) Y-linked traits typically disappear in fourth- or fifth-generation males in the same family.
E) All of these choices are correct.
G) B) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
In humans, one reason why mitochondrial inheritance is strikingly different from nuclear inheritance is that:
A) mitochondrial DNA is single-stranded.
B) mitochondrial DNA is circular.
C) unlike nuclear inheritance, both parents do not contribute mitochondrial DNA.
D) unlike mitochondrial inheritance, only one parent contributes nuclear DNA.
E) mitochondrial inheritance is sex-linked.
G) C) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The Y chromosome can be used to trace ancestry because:
A) natural selection favors specific mutations in specific places.
B) mutations in the Y chromosome occurred as people migrated around the globe.
C) mutations in the Y chromosome are independent of mutations in mitochondria.
D) mutations in the Y chromosome occur only in a few locations.
E) nonmutant Y chromosome genotypes are eliminated from human populations.
G) A) and E)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
The fruit fly cross shown here analyzes the transmission of two genes in the X chromosome. The male parent has mutant alleles for both the white gene (w-) and the crossveinless gene (cv-) . The female parent has nonmutant forms of these genes (w+ and cw+) . A cross between siblings of the F1 generation-a red-eyed, crossveined female and a red-eyed, crossveined male-generates F2 progeny. Examine the genotype of the F2 male progeny. Notice that the progeny fall into two groups. Refer to the figure below when answering the following question. Which of the statements below does NOT explain why the male progeny from the F1 cross are used for linkage analysis? 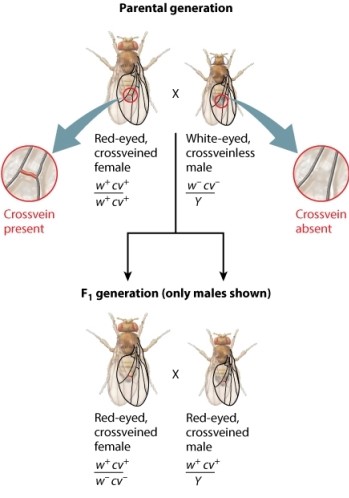
A) The phenotype of F2 males reveals the genotype of the X chromosome they inherited from their mother.
B) All four possible classes of maternal gametes are observed in the F2 male progeny in a 1:1:1:1 ratio, which indicates that the two genes undergo independent assortment.
C) The lack of independent assortment indicates that the two genes are linked in the X chromosome.
D) The Y chromosome in the male offspring allows the genotype of each X chromosome inherited from the mother to be observed in the male phenotype.
F) B) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
An individual is heterozygous for two linked genes, but whether its genotype is A B/a b or A b/a B is not known. The individual is crossed with a b/a b, and among the progeny are the following: 62 A B/a b 13 A b/a b 18 a B/a b 51 a b/a b These results imply that the genotype of the doubly heterozygous parent was A B/a b.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
True/False
Mitochondrial DNA can be used to trace ancestry and population history.
B) False
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Multiple Choice
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding chloroplast inheritance?
A) Like mitochondria, chloroplasts always demonstrate a maternal pattern of inheritance, regardless of the plant species.
B) Chloroplasts always demonstrate a paternal pattern of inheritance, regardless of the plant species.
C) Chloroplasts always demonstrate biparental inheritance, regardless of the plant species.
D) Chloroplasts can demonstrate maternal, paternal, or biparental patterns of inheritance depending on the plant species.
F) A) and C)
Correct Answer

verified
Correct Answer
verified
Showing 81 - 100 of 201
Related Exams